 |
Caution: Federal (USA) law prohibits dispensing without prescription.
|
NOTE:
|
ActHIB®, Haemophilus b Conjugate Vaccine (Tetanus Toxoid Conjugate), produced by Aventis Pasteur SA, is a sterile, lyophilized powder which is reconstituted at the time of use with either saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride) or Aventis Pasteur Inc. (AvP) Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed (whole-cell pertussis vaccine DTP) or Tripedia®, AvP Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed (DTaP) (when reconstituted known as TriHIBit®) for intramuscular use only. The vaccine consists of the Haemophilus b capsular polysaccharide (polyribosyl-ribitol-phosphate, PRP), a high molecular weight polymer prepared from the Haemophilus influenzae type b strain 1482 grown in a semi-synthetic medium, covalently bound to tetanus toxoid. 1 The lyophilized ActHIB® powder and saline diluent contain no preservative. The tetanus toxoid is prepared by extraction, ammonium sulfate purification, and formalin inactivation of the toxin from cultures of Clostridium tetani (Harvard strain) grown in a modified Mueller and Miller medium. 2 The toxoid is filter sterilized prior to the conjugation process. Potency of ActHIB® is specified on each lot by limits on the content of PRP polysaccharide and protein in each dose and the proportion of polysaccharide and protein in the vaccine which is characterized as high molecular weight conjugate.
When ActHIB® is reconstituted with saline diluent, each single dose of 0.5 mL is formulated to contain 10 µg of purified capsular polysaccharide conjugated to 24 µg of inactivated tetanus toxoid, and 8.5% of sucrose.
When ActHIB® is combined with AvP DTP vaccine by reconstitution, each single dose (0.5 mL) is formulated to contain 10 µg of purified capsular polysaccharide conjugated to 24 µg of inactivated tetanus toxoid, 8.5% of sucrose, 6.7 Lf of diphtheria toxoid, 5 Lf of tetanus toxoid and an estimate of 4 protective units of pertussis vaccine. Thimerosal (mercury derivative) 1:10,000 is added as a preservative to AvP DTP vaccine. (Refer to product insert for AvP whole-cell DTP.)
When ActHIB® is combined with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) by reconstitution for booster dose , each single dose (0.5 mL) is formulated to contain 10 µg of purified capsular polysaccharide conjugated to 24 µg of inactivated tetanus toxoid, 8.5% of sucrose, 6.7 Lf of diphtheria toxoid, 5 Lf of tetanus toxoid and 46.8 µg of pertussis antigens. Thimerosal (mercury derivative) 1:10,000 is added as a preservative to Tripedia®. (Refer to product insert for Tripedia®.)
The reconstituted vaccine, using saline diluent, appears clear and colorless. The reconstituted vaccine, using AvP DTP vaccine, appears whitish in color. TriHIBit®, the reconstituted vaccine, using Tripedia®, is a homogenous white suspension.
|
NOTE:
|
H influenzae type b was the leading cause of invasive bacterial disease among children in the United States prior to licensing of Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines. Based on its active surveillance areas, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) now estimate that H influenzae type b disease in children under the age of 5 years has been reduced by 95%. 3 Before effective vaccines were introduced, it was estimated that one in 200 children developed invasive H influenzae type b disease by the age of 5 years. In children less than 5 years of age, the mortality rate for invasive H influenzae type b disease ranged between 3% and 6%. 3 In more than 60% of these children, meningitis was the clinical syndrome and permanent sequelae ranging from mild hearing loss to mental retardation affecting 20% to 30% of all survivors. 3 Ninety-five percent of the cases of invasive H influenzae disease among children < 5 years of age were caused by organisms with the type b polysaccharide capsule. Approximately two-thirds of all cases of invasive H influenzae type b disease affected infants and children < 15 months of age, a group for which a vaccine was not available until late 1990. 4,5
Incidence rates of invasive H influenzae type b disease have been shown to be increased in certain high-risk groups, such as native Americans (both American Indians and Eskimos), blacks, individuals of lower socioeconomic status, and patients with asplenia, sickle cell disease, Hodgkin' disease, and antibody deficiency syndromes. 5,6 Studies also have suggested that the risk of acquiring primary invasive H influenzae type b disease for children under 5 years of age appears to be greater for those who attend day-care facilities. 7,8,9,10
The potential for person to person transmission of the organism among susceptible individuals has been recognized. Studies of secondary spread of disease in household contacts of index patients have shown a substantially increased risk among exposed household contacts under 4 years of age. 11 Adults can be colonized with H influenzae type b from children infected with the organism. 12
The response to ActHIB® is typical of a T-dependent immune response to antigen. The prominent isotype of anti-capsular PRP antibody induced by ActHIB® is IgG. 13 A substantial booster response has been demonstrated in children 12 months of age or older who previously received two or three doses. Bactericidal activity against H influenzae type b is demonstrated in serum after immunization and statistically correlates with the anti-PRP antibody response induced by ActHIB®. 14
Antibody to H influenzae capsular polysaccharide (anti-PRP) titers of > 1.0 µg/mL following vaccination with unconjugated PRP vaccine correlated with long-term protection against invasive H influenzae type b disease in children older than 24 months of age. 15 Although the relevance of this threshold to clinical protection after immunization with conjugate vaccines is not known, particularly in light of the induced, immunologic memory, this level continues to be considered as indicative of long-term protection. 4 The immunogenicity and safety of ActHIB® has been demonstrated in the United States and worldwide. ActHIB® induced, on average anti-PRP levels >/= 1.0 µg/mL in 90% of infants after the primary series and in more than 98% of infants after a booster dose. 14
Two clinical trials supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have compared the anti-PRP antibody responses to three Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines in racially mixed populations of children. These studies were done in Tennessee 16 (Table 1) and in Minnesota, Missouri and Texas 17 (Table 2) in infants immunized with ActHIB® and other Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. All Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines were administered concomitantly with Poliovirus Vaccine Live Oral and DTP vaccines at separate sites.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Native American populations have had high rates of H influenzae type b disease and have been observed to have low immune responses to Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines. Following three doses of ActHIB® at six weeks, four and six months of age, 75% of Native Americans in Alaska showed an anti-PRP antibody titer of >/= 1.0 µg/mL. 18
Children 12 to 24 months of age who had not previously received Haemophilus b conjugate vaccination were immunized with a single dose of ActHIB®. GMT anti-PRP antibody responses were 5.12 µg/mL (90% responding with >/= 1.0 µg/mL) for children 12 to 15 months of age and 4.4 µg/mL (82% responding with >/= 1.0 µg/mL) for children 17 to 24 months of age. 18
These trials demonstrated that ActHIB® consistently conferred an anti-PRP antibody response previously shown to correlate with protection, when administered either as a regimen of three doses at least four to eight weeks apart in infants 2 to 6 months of age or as a single dose in children 12 months of age and older. 18
ActHIB® has been found to be immunogenic in children with sickle cell anemia, a condition which may cause increased susceptibility to Haemophilus b disease. Two doses of ActHIB® given at two-month intervals induced anti-PRP antibody titers of 1.0 µg/mL in 89% of these children with a mean age of 11 months. This is comparable to anti-PRP antibody levels demonstrated in normal children of similar age following two doses of ActHIB®. 19
ActHIB® COMBINED WITH WHOLE-CELL PERTUSSIS VACCINE (DTP) BY RECONSTITUTION FOR PRIMARY IMMUNIZATION
Comparative clinical trials demonstrated that a similar anti-PRP response was achieved in infants as young as 2 months old when one dose of AvP whole-cell DTP vaccine was used to reconstitute lyophilized ActHIB® (Table 3). 14,18
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Antibody responses to diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis antigens were also measured in this trial. Post dose three antibody responses to all measured vaccine antigens were similar, within each study, when infants who received the combined vaccine were compared to infants who received whole-cell DTP and ActHIB® separately. Interference with the antibody response to the pertussis component has been suggested with a DTP vaccine unlicensed in the US. 20 Percentages of subjects achieving antibody titers over 1 µg/mL and GMT to PRP in 2-month-old infants following immunization with ActHIB® combined with AvP DTP by reconstitution was similar when compared to infants who received DTP and ActHIB® separately (84% versus 85% and 4.3 µg/mL versus 4.8 µg/mL). 14,18
TriHIBit®, ActHIB® COMBINED WITH TRIPEDIA® VACCINE BY RECONSTITUTION FOR BOOSTER DOSE
Randomized comparative clinical trials demonstrated that the anti-PRP response achieved in 15 to 20-month-old children after one dose of TriHIBit®, Tripedia® and ActHIB® combination vaccine, was similar to that achieved when the two vaccines were given concomitantly at different sites with separate needles and syringes (Table 4). 18 All children had received three doses of a Haemophilus b conjugate vaccine (HibTITER® or ActHIB®) and three doses of a whole-cell DTP vaccine prior to entry into this clinical trial.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Geometric mean titers in response to diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (PT and FHA) were also similar between groups. (Refer to product insert for Tripedia®.) A difference in four-fold antibody response to FHA was noted in this trial. However, the clinical significance of this difference is not known at present.
|
NOTE:
|
ActHIB® or ActHIB® combined with AvP DTP vaccine by reconstitution is indicated for the active immunization of infants and children 2 through 18 months of age for the prevention of invasive disease caused by H influenzae type b and/or diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis.
TriHIBit®, ActHIB® combined with Tripedia® by reconstitution, is indicated for the active immunization of children 15 to 18 months of age for prevention of invasive disease caused by H influenzae type b and diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis.
Antibody levels associated with protection may not be achieved earlier than two weeks following the last recommended dose.
Only AvP whole-cell DTP, Tripedia® or 0.4% Sodium Chloride diluent may be used for reconstitution of lyophilized ActHIB®. TriHIBit®, ActHIB® combined with Tripedia® by reconstitution, should not be administered to infants younger than 15 months of age.
As with any vaccine, vaccination with ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or 0.4% Sodium Chloride diluent may not protect 100% of susceptible individuals.
A single injection containing diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and Haemophilus b conjugate antigens may be more acceptable to parents and may increase compliance with vaccination programs. Therefore, in these situations it may be the judgment of the physician that it is of benefit to administer a single injection of whole-cell DTP or DTaP Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines.
ActHIB® IS CONTRAINDICATED IN CHILDREN WITH A HISTORY OF HYPERSENSITIVITY TO ANY COMPONENT OF THE VACCINE AND TO ANY COMPONENT OF DTP OR Tripedia® WHEN COMBINED BY RECONSTITUTION WITH THESE VACCINES. ANY CONTRAINDICATION FOR DTP IS A CONTRAINDICATION FOR ActHIB® RECONSTITUTED WITH DTP. ANY CONTRAINDICATION FOR Tripedia® IS A CONTRAINDICATION FOR TriHIBit®, ActHIB® RECONSTITUTED WITH Tripedia®. (Refer to product inserts for AvP whole-cell DTP and Tripedia®.)
This product contains dry natural latex rubber as follows: The stopper to the diluent vial contains dry natural latex rubber. The lyophilized vaccine vial contains no rubber of any kind.
If ActHIB® or ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) is administered to immunosuppressed persons or persons receiving immunosuppressive therapy, the expected antibody responses may not be obtained. This includes patients with asymptomatic or symptomatic HIV-infection, 21 severe combined immunodeficiency, hypogammaglobulinemia, or agammaglobulinemia; altered immune states due to diseases such as leukemia, lymphoma, or generalized malignancy; or an immune system compromised by treatment with corticosteroids, alkylating drugs, antimetabolites or radiation. 22 (Refer to product inserts for AvP whole-cell DTP and Tripedia®.)
TriHIBit®, ActHIB® combined with Tripedia® by reconstitution, should not be administered to infants younger than 15 months of age.
GENERAL
Care is to be taken by the health-care provider for the safe and effective use of this vaccine.
EPINEPHRINE INJECTION (1:1000) MUST BE IMMEDIATELY AVAILABLE SHOULD AN ANAPHYLACTIC OR OTHER ALLERGIC REACTIONS OCCUR DUE TO ANY COMPONENT OF THE VACCINE.
Prior to an injection of any vaccine, all known precautions should be taken to prevent adverse reactions. This includes a review of the patient's history with respect to possible sensitivity and any previous adverse reactions to the vaccine or similar vaccines, and to possible sensitivity to dry natural latex rubber, previous immunization history, current health status (see CONTRAINDICATIONS ; sections), and a current knowledge of the literature concerning the use of the vaccine under consideration. (Refer to product inserts for AvP whole-cell DTP and Tripedia®.)
The health-care provider should ask the parent or guardian about the recent health status of the infant or child to be immunized including the infant' or child's previous immunization history prior to administration of ActHIB®, AvP DTP and Tripedia®.
Minor illnesses such as upper respiratory infection with or without low-grade fever are not contraindications for use of ActHIB®. 23
As reported with Haemophilus b polysaccharide vaccines, 24 cases of H influenzae type b disease may occur subsequent to vaccination and prior to the onset of protective effects of the vaccine. 18 (See section.)
The evidence favors rejection of a causal relation between immunization with Hib conjugate vaccines and early-onset of Hib disease. 25
Antigenuria has been detected in some instances following receipt of ActHIB®; therefore, urine antigen detection may not have definitive diagnostic value in suspected H influenzae type b disease within one week of immunization. 26
Special care should be taken to ensure that ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or Tripedia® or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride) is not injected into a blood vessel.
Administration of ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride) is not contraindicated in individuals with HIV infection. 22
A separate, sterile syringe and needle or a sterile disposable unit should be used for each patient to prevent transmission of hepatitis or other infectious agents from person to person. Needles should not be recapped and should be properly disposed.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENT
The health-care provider should inform the parent or guardian of the benefits and risks of the vaccine.
Prior to administration of ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride), the parent or guardian should be asked about the recent health status of the infant or child to be immunized.
The physician should inform the parent or guardian about the significant adverse reactions that have been temporally associated with the administration of ActHIB® reconstituted with saline or DTP, or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®). The parent or guardian should be instructed to report any serious adverse reactions to their health-care provider.
As part of the child's immunization record, the date, lot number and manufacturer of the vaccine administered should be recorded. 27,28,29
The US Department of Health and Human Services has established a new Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) to accept all reports of suspected adverse events after the administration of any vaccine, including but not limited to the reporting of events required by the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act of 1986. 27 The toll-free number for VAERS forms and information is 1-800-822-7967.
The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program, established by the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act of 1986, requires physicians and other health-care providers who administer vaccines to maintain permanent vaccination records and to report occurrences of certain adverse events to the US Department of Health and Human Services. Reportable events include those listed in the Act for each vaccine and events specified in the package insert as contraindications to further doses of the vaccine. 28,29
The health-care provider should inform the parent or guardian of the importance of completing the immunization series.
The health-care provider should provide the Vaccine Information Materials (VIMs) which are required to be given with each immunization.
When AvP DTP is used to reconstitute ActHIB® or Tripedia® is used to reconstitute ActHIB® (TriHIBit®) and administered to immunosuppressed persons or persons receiving immunosuppressive therapy, the expected antibody response may not be obtained.
Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, and corticosteroids (used in greater than physiologic doses), may reduce the immune response to vaccines. Short-term (< 2 weeks) corticosteroid therapy or intra-articular, bursal, or tendon injections with corticosteroids should not be immunosuppressive. Although no specific studies with pertussis vaccine are available, if immunosuppressive therapy will be discontinued shortly, it is reasonable to defer vaccination until the patient has been off therapy for one month; otherwise, the patient should be vaccinated while still on therapy. 23
If ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) has been administered to persons receiving immunosuppressive therapy, a recent injection of immunoglobulin or having an immunodeficiency disorder, an adequate immunologic response may not be obtained.
In clinical trials, ActHIB® was administered, at separate sites, concomitantly with one or more of the following vaccines: DTP, DTaP, Poliovirus Vaccine Live Oral (OPV), Measles, Mumps and Rubella vaccine (MMR), Hepatitis B vaccine and occasionally Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine (IPV). No impairment of the antibody response to the individual antigens, diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis, was demonstrated when ActHIB® was given at the same time, at separate sites, with IPV or MMR. 18 In addition, more than 47,000 infants in Finland have received a third dose of ActHIB® concomitantly with MMR vaccine with no increase in serious or unexpected adverse events. 18
No significant impairment of antibody response to Measles, Mumps and Rubella was noted in 15- to 20-month-old children who received TriHIBit®, ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia®, concomitantly with MMR. No data are available to the manufacturer concerning the effects of immune response of OPV, IPV or Hepatitis B vaccine when given concurrently with ActHIB® reconstituted with 0.4% Sodium Chloride or AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®). 18
As with other intramuscular injections, use with caution in patients on anticoagulant therapy.
CARCINOGENESIS, MUTAGENESIS, IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) has not been evaluated for its carcinogenic, mutagenic potential or impairment of fertility.
PREGNANCY
REPRODUCTIVE STUDIES--PREGNANCY CATEGORY C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride). It is also not known whether ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride) can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride) is NOT recommended for use in a pregnant woman and is not approved for use in children 5 years of age or older.
PEDIATRIC USE
SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF TriHIBit®, ActHIB® RECONSTITUTED WITH Tripedia®, IN INFANTS BELOW THE AGE OF 15 MONTHS HAVE NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section.)
SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF ActHIB® RECONSTITUTED WITH AvP DTP OR SALINE DILUENT (0.4% SODIUM CHLORIDE) IN INFANTS BELOW THE AGE OF SIX WEEKS HAVE NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section.)
|
NOTE:
|
More than 7,000 infants and young children (</= 2 years of age) have received at least one dose of ActHIB® during US clinical trials. Of these, 1,064 subjects 12 to 24 months of age who received ActHIB® alone reported no serious or life threatening adverse reactions.
Adverse reactions commonly associated with a first ActHIB® immunization of children 12 to 15 months of age who were previously unimmunized with any Haemophilus b conjugate vaccine, include local pain, redness and swelling at the injection site. Systemic reactions include fever, irritability and lethargy. 14,18
In a multicenter trial, ActHIB® was administered to US infants at 2, 4, and 6 months of age concomitantly, at separate sites, with AvP DTP. The adverse events observed are summarized in Table 5.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In general, the rates of minor systemic reactions after ActHIB® and DTP immunization were comparable to those usually reported after DTP vaccine alone. 30,31,32,33
When ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP whole-cell DTP was administered in infants at 2, 4, and 6 months of age, the systemic adverse experience profile (Table 6) was comparable to that observed when the two vaccines were given separately (Table 5). An increase in the rates of local reactions was observed within the 24-hour period after immunization. 18
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In a third US trial when ActHIB® was combined with DTP by reconstitution, approximately 1,450 doses were administered to infants starting at 2 months of age. Adverse reactions observed at 6 and 24 hours respectively after the first immunization (n = 498) were tenderness 66.9% and 30.7%; erythema (> 1") 8.6% and 2.2%; induration 38.2% and 21.7%; irritability 77.9% and 35.7%; drowsiness 63.7% and 34.1%; anorexia 26.1% and 12.9%; diarrhea 6.8% and 9.0%; and vomiting 3.4% and 3.8%. 18 One hypotonic/hyporesponsive episode (HHE) was seen in an infant following the second dose in this trial. This is consistent with the HHE incidence rate observed with DTP vaccination alone. 4
Adverse reactions associated with ActHIB® generally subsided after 24 hours and usually do not persist beyond 48 hours after immunization.
No data are available on the safety of a booster dose of ActHIB® combined with AvP DTP vaccine by reconstitution given in 15 to 20-month-old children.
In a US trial, safety of TriHIBit®, ActHIB® combined with Tripedia® by reconstitution, in 110 children aged 15 to 20 months was compared to ActHIB® given with Tripedia® at separate sites to 110 children. All children received three doses of Haemophilus b conjugate vaccine (ActHIB® or HibTITER®) and three doses of whole-cell DTP at approximately 2, 4 and 6 months of age.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TriHIBit®, ActHIB® combined with Tripedia® by reconstitution, and administered to approximately 850 children, aged 15 to 20 months. All children received three doses of a Haemophilus b conjugate vaccine (ActHIB® or HibTITER®) and three doses of whole-cell DTP at approximately 2, 4, and 6 months of age. Local reactions were typically mild and usually resolved within the 24 to 48 hour period after immunization. The most common local reactions were pain and tenderness at the injection site. Systemic reactions occurring were usually mild and resolved within 72 hours of immunization. The reaction rates were similar to those observed in Table 7 when TriHIBit®, ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® was administered and when Tripedia® was administered alone as a booster. 18
In a randomized, double-blind US clinical trial, ActHIB® was given concomitantly with DTP to more than 5,000 infants and hepatitis B vaccine was given with DTP to a similar number. In this large study, deaths due to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and other causes were observed but were not different in the two groups. In the first 48 hours following immunization, two definite and three possible seizures were observed after ActHIB® and DTP in comparison with none after Hepatitis B vaccine and DTP. 18 This rate of seizures following ActHIB® and DTP was not greater than previously reported in infants receiving DTP alone. (Refer to product insert for AvP DTP.) Other adverse reactions reported with administration of other Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines include urticaria, seizures, hives, renal failure and Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). 18,34 A cause and effect relationship among any of these events and the vaccination has not been established.
When ActHIB® was given with DTP and inactivated poliovirus vaccine to more than 100,000 Finnish infants, the rate and extent of serious adverse reactions were not different from those seen when other Haemophilus b conjugate vaccines were evaluated in Finland (i.e. HibTITER®, ProHIBit®). 18
However, the number of subjects studied with TriHIBit®, ActHIB® combined with Tripedia® by reconstitution, was inadequate to detect rare serious adverse events.
Reporting by the parent or guardian of all adverse events occurring after vaccine administration should be encouraged. Adverse events following immunization with vaccine should be reported by the health-care provider to the US Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Reporting forms and information about reporting requirements or completion of the form can be obtained from VAERS through a toll-free number 1-800-822-7967. 26,27,28
Health-care providers also should report these events to the Director of Scientific and Medical Affairs, Aventis Pasteur Inc., Discovery Drive, Swiftwater, PA 18370 or call 1-800-822-2463.
|
NOTE:
|
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and/or discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. If these conditions exist, the vaccine should not be administered.
Using Aventis Pasteur Inc. DTP, cleanse both the DTP and ActHIB® vial rubber stoppers with a suitable germicide prior to reconstitution. Thoroughly agitate the vial of AvP DTP then withdraw a 0.6 mL dose and inject into the vial of lyophilized ActHIB®. After reconstitution and thorough agitation, the combined vaccines will appear whitish in color. Withdraw and administer 0.5 mL dose of the combined vaccines intramuscularly. Vaccine should be used within 24 hours after reconstitution. Refer to Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
To prepare TriHIBit®, cleanse both the Tripedia® and ActHIB® vial rubber stoppers with a suitable germicide prior to reconstitution. Thoroughly agitate the vial of AvP Tripedia® then withdraw a 0.6 mL dose and inject into the vial of lyophilized ActHIB®. After reconstitution and thorough agitation, the combined vaccines will appear whitish in color. Withdraw and administer 0.5 mL dose of the combined vaccines intramuscularly. Vaccine should be used immediately (within 30 minutes) after reconstitution. Refer to Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
Using saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride) cleanse the vaccine vial rubber stopper with a suitable germicide and inject the entire volume of diluent contained in the vial or syringe into the vial of lyophilized vaccine. Thorough agitation is advised to ensure complete reconstitution. The entire volume of reconstituted vaccine is then drawn back into the syringe before injecting one 0.5 mL dose intramuscularly. The vaccine will appear clear and colorless. Vaccine should be used within 24 hours after reconstitution. Refer to Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR RECONSTITUTION OF ActHIB® WITH AvP DTP OR RECONSTITUTION OF ActHIB® WITH TRIPEDIA® (TriHIBit®) OR SALINE DILUENT (0.4% SODIUM CHLORIDE):
 |
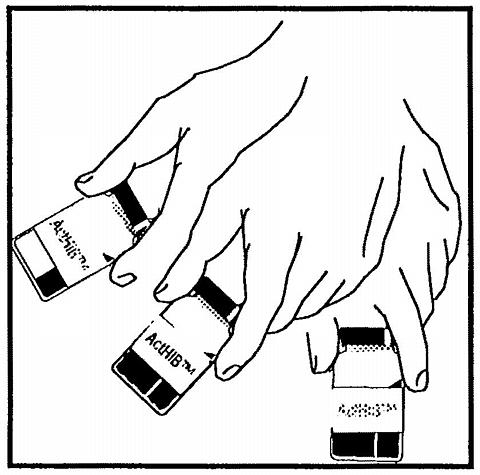
Figure 1. Cleanse stopper and agitate the vial of DTP, Tripedia®, or 0.4% Sodium Chloride used to reconstitute ActHIB®.
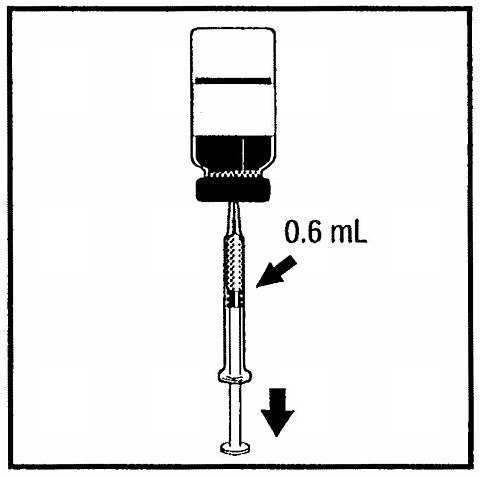 |
Figure 2. Withdraw volume of DTP, Tripedia®, or 0.4% Sodium Chloride as indicated.
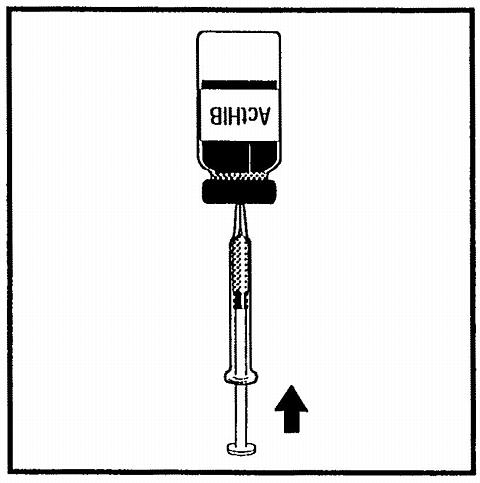 |
Figure 3. Cleanse the ActHIB® stopper, insert syringe needle through the rubber stopper and inject volume as directed.
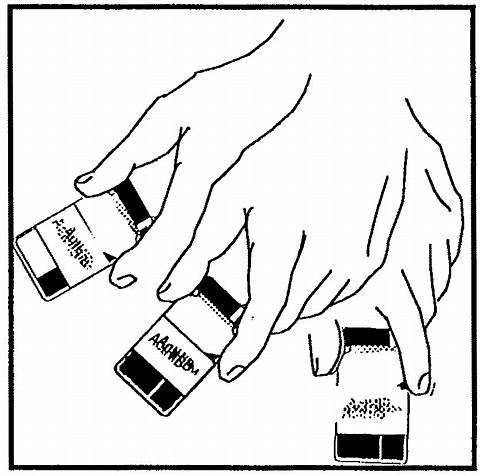 |
Figure 4. Agitate vial thoroughly.
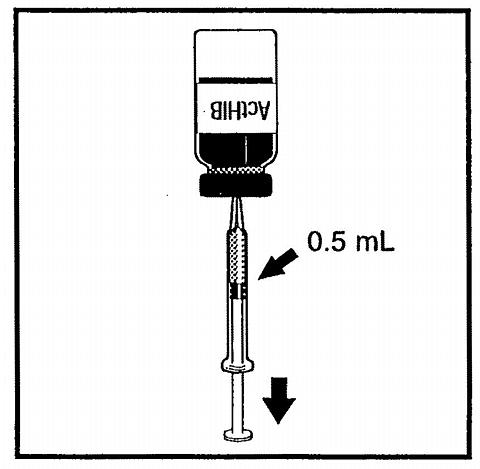 |
Figure 5. After reconstitution with either DTP, or reconstitution with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or 0.4% Sodium Chloride withdraw 0.5 mL of reconstituted vaccine and administer intramuscularly.
Before injection, the skin over the site to be injected should be cleansed with a suitable germicide. After insertion of the needle, aspirate to ensure that the needle has not entered a blood vessel.
DO NOT INJECT INTRAVENOUSLY.
Each dose of ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride) is administered intramuscularly in the outer aspect of the vastus lateralis (mid-thigh) or deltoid. The vaccine should not be injected into the gluteal area or areas where there may be a nerve trunk. During the course of primary immunizations, injections should not be made more than once at the same site.
When ActHIB® is reconstituted with AvP DTP, the combined vaccines are indicated for infants and children 2 through 18 months of age for intramuscular administration in accordance with the schedule indicated in Table 8. 14 When ActHIB® is reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®), the combined vaccines are indicated for children 15 to 18 months of age for intramuscular administration in accordance with the schedule in Table 8. 14
|
The number of doses of Haemophilus b Conjugate Vaccine indicated depends on the age at which immunization is begun. A child 7 to 11 months of age should receive 2 doses of Haemophilus b Conjugate Vaccine at 8-week intervals and a booster dose at 15 to 18 months of age. A child 12 to 14 months of age should receive 1 dose of Haemophilus b Conjugate Vaccine followed by a booster 2 months later.
Preterm infants should be vaccinated according to their chronological age from birth. 35
Interruption of the recommended schedule with a delay between doses should not interfere with the final immunity achieved with ActHIB® reconstituted with AvP DTP or ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia® (TriHIBit®) or saline diluent (0.4% Sodium Chloride). There is no need to start the series over again, regardless of the time elapsed between doses.
It is acceptable to administer a booster dose of TriHIBit®, ActHIB® reconstituted with Tripedia®, following a primary series of Haemophilus b conjugate and whole-cell DTP vaccines, or a primary series of a combination vaccine containing whole-cell DTP.
ActHIB® RECONSTITUTED WITH WHOLE-CELL DTP
Vial, 1 Dose, lyophilized vaccine (10 × 1 Dose vials per package), packaged with one 7.5 mL vial of Aventis Pasteur Inc. Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Pertussis Vaccine as Diluent--Product No. 49281-549-10
ActHIB® RECONSTITUTED WITH 0.4% SODIUM CHLORIDE DILUENT
Vial, 1 Dose, lyophilized vaccine (5 × 1 Dose vials per package), packaged with 0.6 mL vial containing diluent (5 × 0.6 mL vials per package)--Product No. 49281-545-05
Administer vaccine within 24 hours after reconstitution.
TriHIBit®, ActHIB® RECONSTITUTED WITH TRIPEDIA®
Vial, 1 Dose, lyophilized vaccine (10 × 1 Dose vials per package), packaged with one 7.5 mL vial of Tripedia® as Diluent--Product No. 49281-557-10
Vial, 1 Dose, lyophilized vaccine (5 × 1 Dose vials per package), packaged with five 1 Dose vials of Tripedia® as Diluent--Product No. 49281-557-05
Administer vaccine immediately (within 30 minutes) after reconstitution.
Store lyophilized vaccine packaged with saline diluent, Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Pertussis or Tripedia® between 2°-8°C (35°-46°F). DO NOT FREEZE.
Product information
as of September 1996
Manufactured by:
Aventis Pasteur SA
Lyon France
US Govt License #1279
Distributed by:
Aventis Pasteur Inc.
Swiftwater PA 18370 USA
1-800-VACCINE (1-800-822-2463) 4187