 |
Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON* (Neomycin Sulfate-Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate) is a topical corticosteroid-antibiotic solution for ophthalmic use.
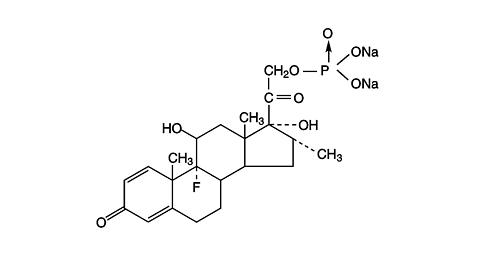
Dexamethasone sodium phosphate is 9-fluoro-11(beta), 17-dihydroxy-16(alpha)-methyl-21-(phosphonooxy)pregna-1, 4-diene-3, 20-dione disodium salt. Its empirical formula is C 22 H 28 FNa 2 O 8 P and its structural formula is:
 |
Dexamethasone is a synthetic analog of naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone and cortisone).
Dexamethasone sodium phosphate is a water soluble, inorganic ester of dexamethasone. Its molecular weight is 516.41.
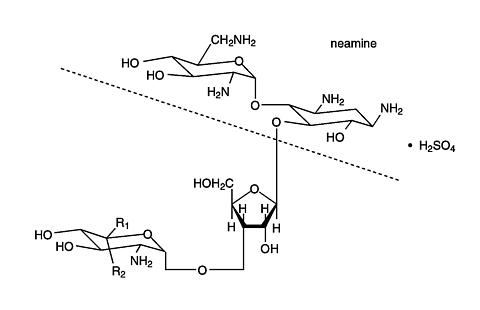
Neomycin sulfate, an antibiotic of the aminoglucoside group, is a mixture of the sulfate salts of neomycin, produced by the growth of Streptomyces fradiae Waksman (Fam. Stretomycetaceae). Neomycin is a complex typically containing 8-13% neomycin C, less than 0.2% neomycin A, and the rest, neomycin B. The empirical formula for both neomycin B and neomycin C is C 23 H 46 N 6 O 13 , and the molecular weight for each is 614.65. Neomycin A (also referred to as neamine) has an empirical formula of C 12 H 26 N 4 O 6 and a molecular weight of 322.36. The structural formulae for neomycin sulfate are:
 |
|
Neomycin B
|
Neomycin C
R 1 =CH 2 NH 2 , R 2 =H |
Each milliliter of buffered Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON in the OCUMETER* ophthalmic dispenser contains: dexamethasone sodium phosphate equivalent to 1 mg (0.1%) dexamethasone phosphate, and neomycin sulfate equivalent to 3.5 mg neomycin base. Inactive ingredients: creatinine, sodium citrate, sodium borate, polysorbate 80, disodium edetate, hydrochloric acid to adjust pH to 6.6-7.2, and water for injection. Benzalkonium chloride 0.02% and sodium bisulfite 0.1% added as preservatives.
*Registered trademark of MERCK & CO., Inc.
Corticosteroids suppress the inflammatory response to a variety of agents, and they probably delay or slow healing. Since corticosteroids may inhibit the body' defense mechanism against infection, a concomitant antimicrobial drug may be used when this inhibition is considered to be clinically significant in a particular case.
When a decision to administer both a corticosteroid and an antimicrobial is made, the administration of such drugs in combination has the advantage of greater patient compliance and convenience, with the added assurance that the appropriate dosage of both drugs is administered, plus assured compatibility of ingredients when both types of drug are in the same formulation and, particularly, that the correct volume of drug is delivered and retained.
The relative potency of corticosteroids depends on the molecular structure, concentration, and release from the vehicle.
Microbiology
The anti-infective component in Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON is included to provide action against specific organisms susceptible to it. Neomycin sulfate is active in vitro against susceptible strains of the following microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella/Enterobacter species, and Neisseria species. The product does not provide adequate coverage against: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens , and streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae . (See .)
For steroid-responsive inflammatory ocular conditions for which a corticosteroid is indicated and where bacterial infection a risk of bacterial ocular infection exists.
Ocular steroids are indicated in inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the globe where the inherent risk of steroid use in certain infective conjunctivitides is accepted to obtain a diminution in edema and inflammation. They are also indicated in chronic anterior uveitis and corneal injury from chemical, radiation, or thermal burns, or penetration of foreign bodies.
The use of a combination drug with an anti-infective component is indicated where the risk of infection is high or where there is an expectation that potentially dangerous numbers of bacteria will be present in the eye.
The particular anti-infective drug in this product is active against the following common bacterial eye pathogens:
Staphylococcus aureus
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella/Enterobacter species
Neisseria species
The product does not provide adequate coverage against:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Serratia marcescens
Streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae
NEODECADRON is contraindicated in most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal diseases of ocular structures. NEODECADRON is also contraindicated in individuals with known or suspected hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients of this preparation, including sulfites, and to other corticosteroids (see ). (Hypersensitivity to the antibiotic component occurs at a higher rate than for other components.)
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in ocular hypertension and/or glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision, and in posterior subcapsular cataract formation.
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections. In those diseases causing thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations have been known to occur with the use of topical corticosteroids. In acute purulent conditions of the eye, corticosteroids may mask infection or enhance existing infection.
If this product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be routinely monitored even though it may be difficult in children and uncooperative patients. Corticosteroids should be used with caution in the presence of ocular hypertension and/or glaucoma. Intraocular pressure should be checked frequently.
The use of corticosteroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of filtering blebs.
Use of ocular corticosteroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex). Employment of a corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution; periodic slit lamp microscopy is essential. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS .)
Neomycin sulfate may occasionally cause cutaneous sensitization. If any reaction indicating such sensitivity is observed, discontinue use.
Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON contains sodium bisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown and probably low. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic people.
General
The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order beyond 20 milliliters should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification, such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining. If signs and symptoms fail to improve after two days, the patient should be re-evaluated.
The possibility of fungal infections of the cornea should be considered after prolonged corticosteroid dosing. Fungal cultures should be taken when appropriate.
If this product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be monitored (see ).
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface. (See PRECAUTIONS , Information for Patients . )
Information for Patients
Patients should be instructed to avoid allowing the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye, eyelid, fingers, or any other surface. The use of this product by more than one person may spread infection. Keep tightly closed when not in use.
Patients should also be instructed that ocular preparations, if handled improperly, can become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated preparations (see PRECAUTIONS , General ).
If redness, irritation, swelling or pain persists or becomes aggravated, the patient should be advised to consult a physician. Patients should also be advised that if they have ocular surgery or develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), they should immediately seek their physician' advice.
One of the preservatives in Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON, benzalkonium chloride, may be absobed by soft contact lenses. Patients wearing soft contact lenses should be instructed to wait at least 15 minutes after instilling Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON before they insert their lenses.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON. Treatment of human lymphocytes in-vitro with neomycin increased the frequency of chromosome aberrations at the highest concentration (80 µg/mL) tested; however, the effects of neomycin on carcinogenesis and mutagenesis in humans are unknown.
Teratogenic effects
Pregnancy Category C.
Corticosteroids have been found to be teratogenic in animal studies. Ocular administration of 0.1% dexamethasone resulted in 15.6% and 32.3% incidence of fetal anomalies in two groups of pregnant rabbits. Fetal growth retardation and increased mortality rates have been observed in rats with chronic dexamethasone therapy. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be observed carefully for signs of hypoadrenalism.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Systemically-administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Adverse reactions have occurred with corticosteroid/anti-infective combination drugs which can be attributed to the corticosteroid component, the anti-infective component, the combination, or any other component of the product. Exact incidence figures are not available since no denominator of treated patients is available.
Reactions occurring most often from the presence of the anti-infective ingredient are allergic sensitizations. The reactions due to the corticosteroid component in decreasing order of frequency are: elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP) with possible development of glaucoma, and infrequent optic nerve damage; posterior subcapsular cataract formation; and delayed wound healing.
Secondary Infection: The development of secondary infection has occurred after use of combinations containing corticosteroids and antimicrobials. Fungal and viral infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term applications of a corticosteroid. The possibility of fungal invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where corticosteroid treatment has been used.
The duration of treatment will vary with the type of lesion and may extend from a few days to several weeks, according to therapeutic response.
Instill one or two drops of Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON into the conjunctival sac every hour during the day and every two hours during the night as initial therapy. When a favorable response is observed, reduce dosage to one drop every four hours. Later, further reduction in dosage to one drop three or four times daily may suffice to control symptoms.
Not more than 20 milliliters should be prescribed initially and the prescription should not be refilled without further evaluation as outlined in PRECAUTIONS above.
Sterile Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution.
No. 7639--Ophthalmic Solution NEODECADRON is supplied as follows:
NDC 0006-7639-03 in 5 mL white opaque, plastic OCUMETER ophthalmic dispenser with a controlled drop tip.
(6505-01-039-4352 0.1% 5 mL).
Store at controlled room temperature, 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). Protect from light.
7261326 Issued December 1995
COPYRIGHT © MERCK & CO., Inc., 1989, 1995
All rights reserved
 |